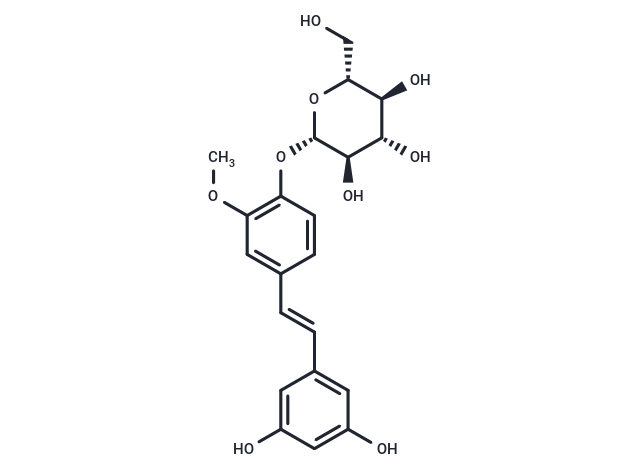
Gnetifolin E
CAS No. 140671-07-4
Gnetifolin E( —— )
Catalog No. M37781 CAS No. 140671-07-4
Gnetifolin E is a new resveratrol trimer derivative from Gnetum brunonianum.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 834 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 1055 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 1406 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 2052 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 2705 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 3573 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGnetifolin E
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionGnetifolin E is a new resveratrol trimer derivative from Gnetum brunonianum.
-
DescriptionGnetifolin E is a resveratrol trimer derivative that can be isolated from Gnetum brunonianum. Gnetifolin E has anti-inflammatory activity, and inhibits TNF-α.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number140671-07-4
-
Formula Weight420.41
-
Molecular FormulaC21H24O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO(C1=C(OC)C=C(/C=C/C2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2)C=C1)[C@@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Yao CS, et al. A new resveratrol trimer derivative from Gnetum brunonianum. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2012;14(9):918-22.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Isorhamnetin 3-robin...
Isorhamnetin 3-O-robinobioside has a great antioxidant and antigenotoxic potential on human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562.
-
PhosTAC7
PhosTAC7 successfully induced ternary protein complex formation and dephosphorylation of phosphatidylserine 318 (pS318) by Halo-FOXO3a in a dose-dependent manner.
-
Echimidine N-oxide
Echimidine N-oxide, a pyrrolizidine alkaloid, exhibits significant inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) with an IC50 value of 0.347 mM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


